How to Install PostgreSQL 13 on Linux Mint 20 Ulyana

PostgreSQL is a powerful, open source object-relational database system with over 30 years of active development that has earned it a strong reputation for reliability, feature robustness, and performance.
PostgreSQL is a free and open-source relational database management system (RDBMS) emphasizing extensibility and SQL compliance.
The PostgreSQL Global Development Group had announced the release of PostgreSQL 13.1 a while ago. This guide will show you how to quickly get PostgreSQL 13.1 up and running on an Linux Mint 20 (Ulyana) system. It will cover from installing PostgreSQL to explore the basics of PostgreSQL database administration, including setting up a new user and database.
Install PostgreSQL 13 on Linux Mint 20 Ulyana
Linux Mint 20 "Ulyana" is built on top of the latest Ubuntu 20.04 LTS "Focal Fossa", so therefore this guide should also be applicable to Ubuntu 20.04 "Focal Fossa" too.
Ubuntu includes PostgreSQL by default, which should be sufficient for
common usage. As the time of this writing, the latest version available on Ubuntu's repository is 12.5-0ubuntu0.20.04.1.
As this guide suggest, we'll install newest version available from PostgreSQL Apt Repository. In that page we'll able to configure what specific version we want to be installed on our system.
Postgresql Apt Repository currently support:
- Debian 9 (stretch), 10 (buster), 11 (bullseye), and unstable (sid)
- Ubuntu 16.04 (xenial), 18.04 (bionic), 20.04 (focal), 20.10 (groovy, amd64 only)
- Architectures: amd64 (64-bit x86), i386 (32-bit x86, being phased out), arm64 (64-bit ARM), ppc64el (little-endian 64-bit POWER)
- PostgreSQL 9.5, 9.6, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14 devel
- Server extensions such as Slony-I, various PL languages, and datatypes
- Applications like pgadmin4, omnidb, pgbouncer, and pgpool-II
Add the PostgreSQL Package Source
We need to create a sources file reflecting the proper PostgreSQL
source for our Linux Mint 20 "Ulyana" distribution. As noted above, we'll use the "focal" release of Ubuntu. We can
accomplish this from the terminal to add the file (make sure to use sudo in all of the following steps):
Add the PGDG APT source file
Create a file at /etc/apt/sources.list.d/postgresql.list with the following command:
$ sudo sh -c 'echo "deb http://apt.postgresql.org/pub/repos/apt/ focal-pgdg main" > \
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/postgresql.list'
Add the PostgreSQL Package Repository Key
Next, add the package repository key:
$ wget --quiet -O - https://www.postgresql.org/media/keys/ACCC4CF8.asc | sudo apt-key add -
Update, Upgrade, and Install PostgreSQL
Update system package source. Once this task is done, we proceed with upgrade packages to the latest versions.
$ sudo apt update
$ sudo apt upgrade
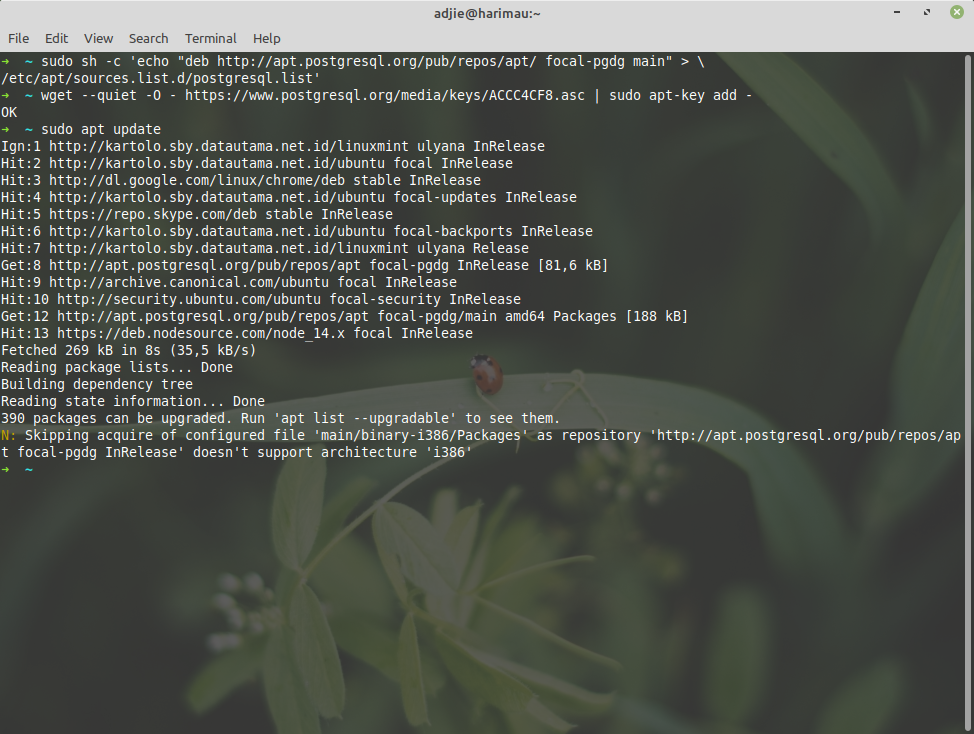
Please note that this can be a long process, depends on your internet connection and how frequent you're upgrading your packages. Also please note that you may be prompted at several points to make some choices about configuration items. Specifically, you may informed that this that or the other configuration file has been changed, and asked if you want to keep your original version, or replace with the package maintainer’s version. Select "Y" to accept the package maintainer’s version in these cases.
Next step is installing PostgreSQL 13:
$ sudo apt install postgresql-13
After pressing "Enter" you will be asked whether to continue with installation or not.After this operation, 58,5 MB of additional disk space will be used.
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
The following additional packages will be installed:
libpq5 pgdg-keyring postgresql-client-13 postgresql-client-common postgresql-common sysstat
Suggested packages:
postgresql-doc-13 libjson-perl isag
The following NEW packages will be installed:
libpq5 pgdg-keyring postgresql-13 postgresql-client-13 postgresql-client-common postgresql-common sysstat
0 upgraded, 7 newly installed, 0 to remove and 390 not upgraded.
Need to get 17,5 MB of archives.
After this operation, 58,5 MB of additional disk space will be used.
Do you want to continue? [Y/n] y
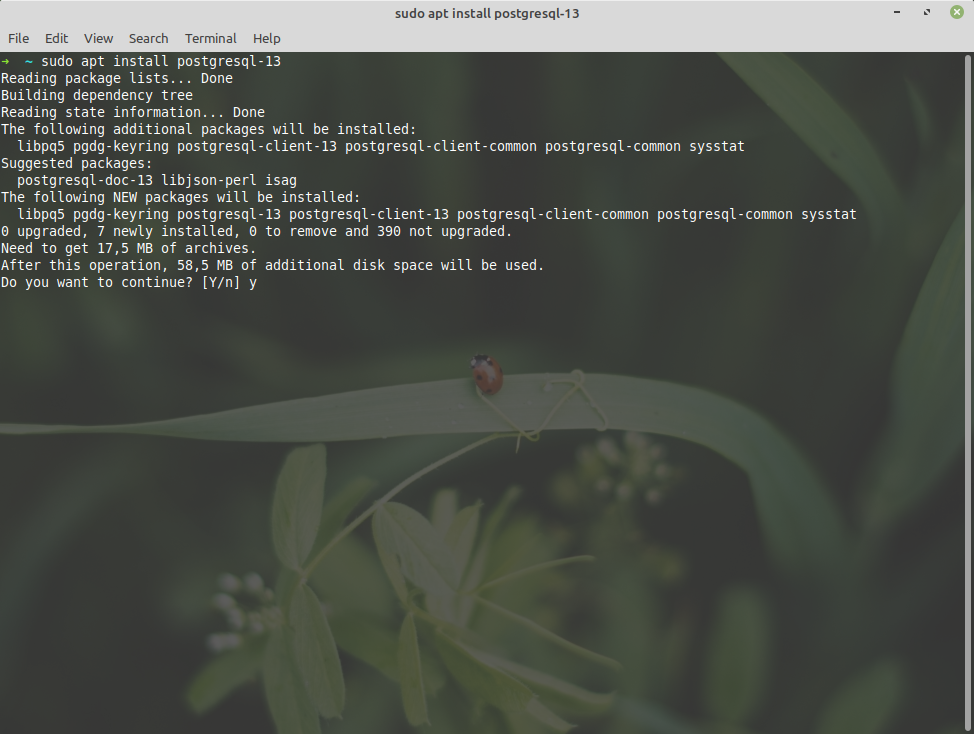
Press "Y" and then "Enter". It will then download all necessary files and continue with installation.
Verify PostgreSQL Installation
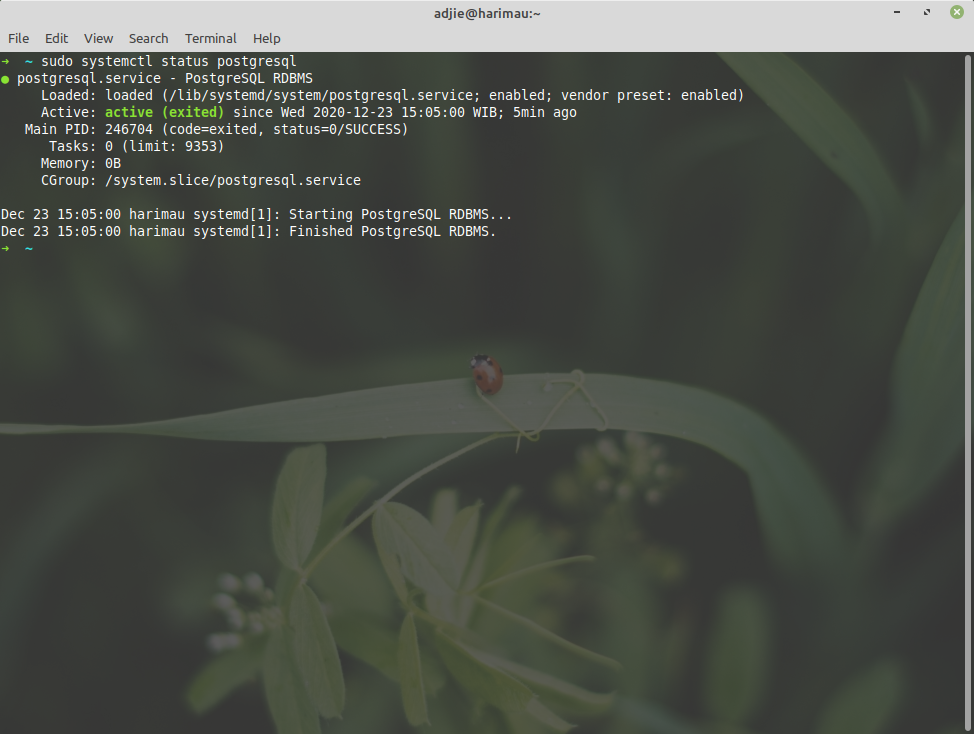
Let's verify that we've installed PostgreSQL correctly. First we'll check if the service is running. Then we can check what version of PostgreSQL server is running.
$ sudo systemctl status postgresql
We can use the psql tool to connect with the PostgreSQL database server and printing its version:
$ psql --version
The output will be something like this: psql (PostgreSQL) 13.1 (Ubuntu 13.1-1.pgdg20.04+1). That’s it. You've successfully installed PostgreSQL 13.1 to your system and you can start using it.
Configuring Postgres for Use
The postgres user
While PostgreSQL become installed, a system user account named postgres was also created with an identical user account in postgres. By default, the postgres
user account isn't configured with a password, so it isn't viable to
log into the server the use of the postgres user account without first
creating a password for it. This postgres account has an all-access pass on your PostgreSQL database server, permission-wise. The postgres user account has similarities to the sa account in SQL server.
The postgres database
PostgreSQL is installed with a default database postgres. For the most part, we use the postgres database for administration functions, and create new databases on the PostgreSQL server to suit our needs.
The psql Command Line Utility
PostgreSQL consists of psql, a command line application for managing your databases and server. While a GUI-based software such as pgadmin3 is often less complicated to use in the daily task, the command line utilty psql is always handy. psql gives total control of your postgres system from the terminal, together with the ability to execute SQL queries.
We will use psql to perform our preliminary configuration and to create an initial database super user.
Create super user account
In this step we will super-user account to deals with our database in the daily task.
To do this, we will get access to the postgres account through your machine root user. Then we'll use that postgres
account to create a brand new super-user account for your PostgreSQL
installation which can be regulated more efficiently. As an example we
will use jason as our new PostgreSQL super-user account.
$ sudo su -
root@harimau:~# su - postgres
postgres@harimau:~$ psql
psql (13.1 (Ubuntu 13.1-1.pgdg20.04+1))
Type "help" for help.
postgres=# CREATE USER jason
postgres-# WITH SUPERUSER CREATEDB CREATEROLE
postgres-# PASSWORD 'youshouldchangethis';
Notice in the above we can enter multiple lines of command in SQL shell. The SQL is not executed until semi-colon followed enter is found. Which means, the semi-colon will make the shell execute entered commands. After pressing "Enter" it will respond with something like this:
CREATE ROLE
postgres=#
Which means we've successfully created this new superuser account.
Login using our newly created account
Let's verify that everything is working correctly. Try to log in with psql using our new super-user account and create a quick test database:
$ psql postgres
psql (13.1 (Ubuntu 13.1-1.pgdg20.04+1))
Type "help" for help.
postgres=#
Note in the above terminal session, we specified the postgres default database when we logged in, since there aren’t yet any other databases to connect to.
Create test database
Next test is to create test database test_database using our new super-user account:
postgres=# CREATE DATABASE test_database WITH OWNER jason;
CREATE DATABASE
postgres=# \connect test_database;
You are now connected to database "test_database" as user "jason".
test_database=#
Final Words
I hope that you now know how to install PostgreSQL 13.1 on Linux Mint 20 Ulyana. If you run into any issues or have any feedback feel free to drop a comment below.


Thanks it's educative for newbies
Thank you very much. I was able to install and confirm it on Linux Mint 20.2 Cinnamon 64 bit without any issues. That was perfect. You are a charm. Could you kindly post an article on how to install pgadmin4? I have checked the pgadmin site https://www.pgadmin.org/download/pgadmin-4-apt/ and there is an installation documentation but it is not as good as your posts.