How to Install Docker on Debian 11 Bullseye

As published on Wikipedia, Docker is a set of platform as a service (PaaS) products that use OS-level virtualization to deliver software in packages called containers. Containers are isolated from one another and bundle their own software, libraries and configuration files; they can communicate with each other through well-defined channels. All containers are run by a single operating-system kernel and are thus more lightweight than virtual machines.
We'll cover the installation of Docker on Debian 11 Bullseye in this article.
Update Local Packages and Install Dependencies
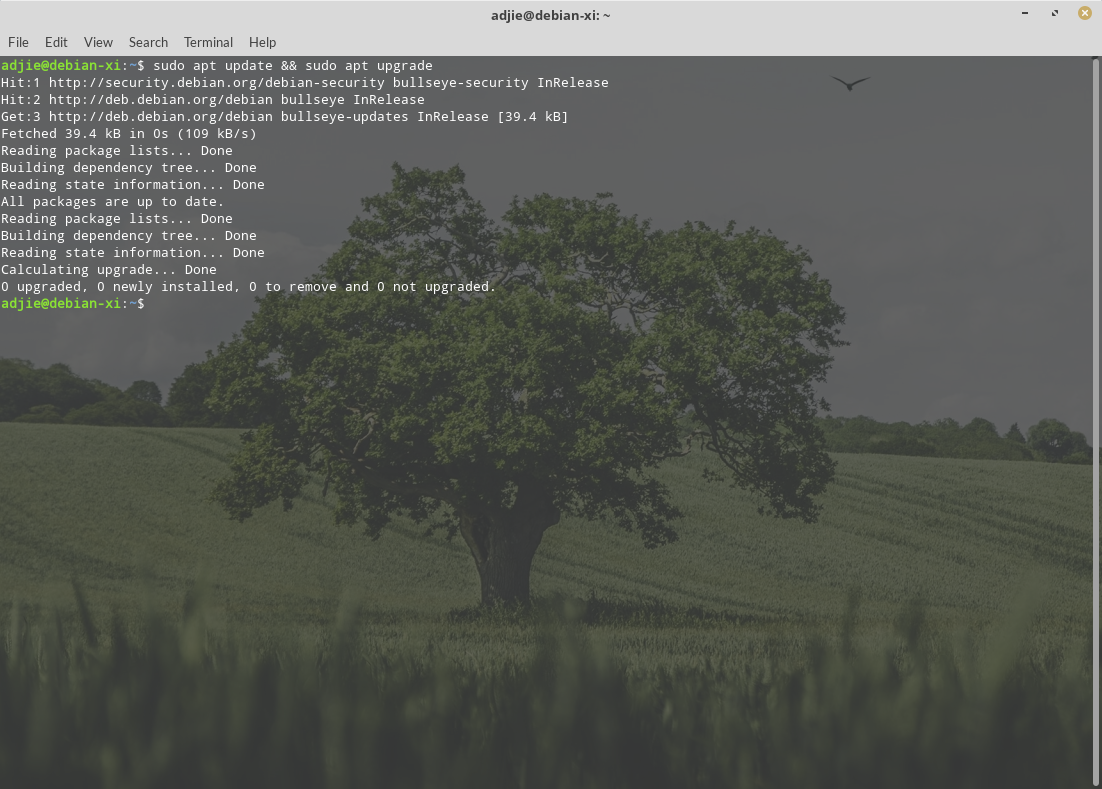
First, make sure our packages are up-to-date. Then, install all the packages used by Docker as dependencies. Open up a terminal and type this command:
$ sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
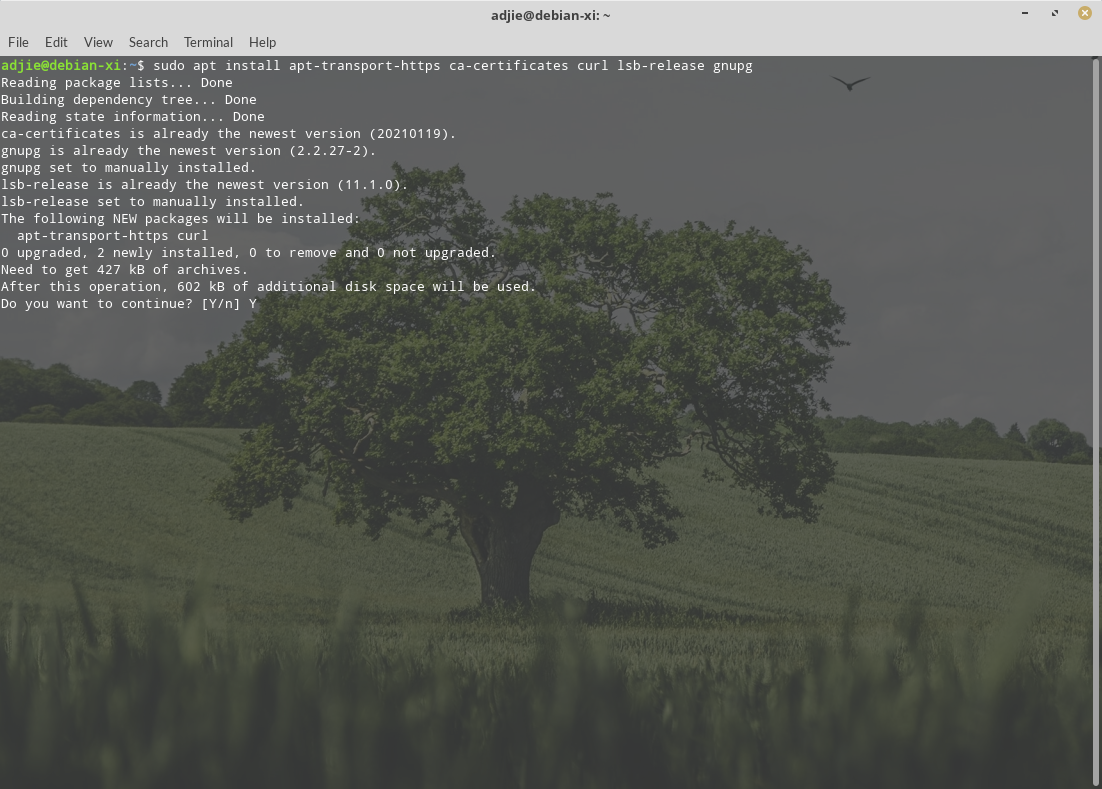
$ sudo apt install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl gnupg lsb-release
Add Docker GPG Key and Repository
We need to add Docker GPG key used for signing Docker packages and add Docker upstream repository to our Debian 11. This is necessary step so we can install the latest stable release of Docker.
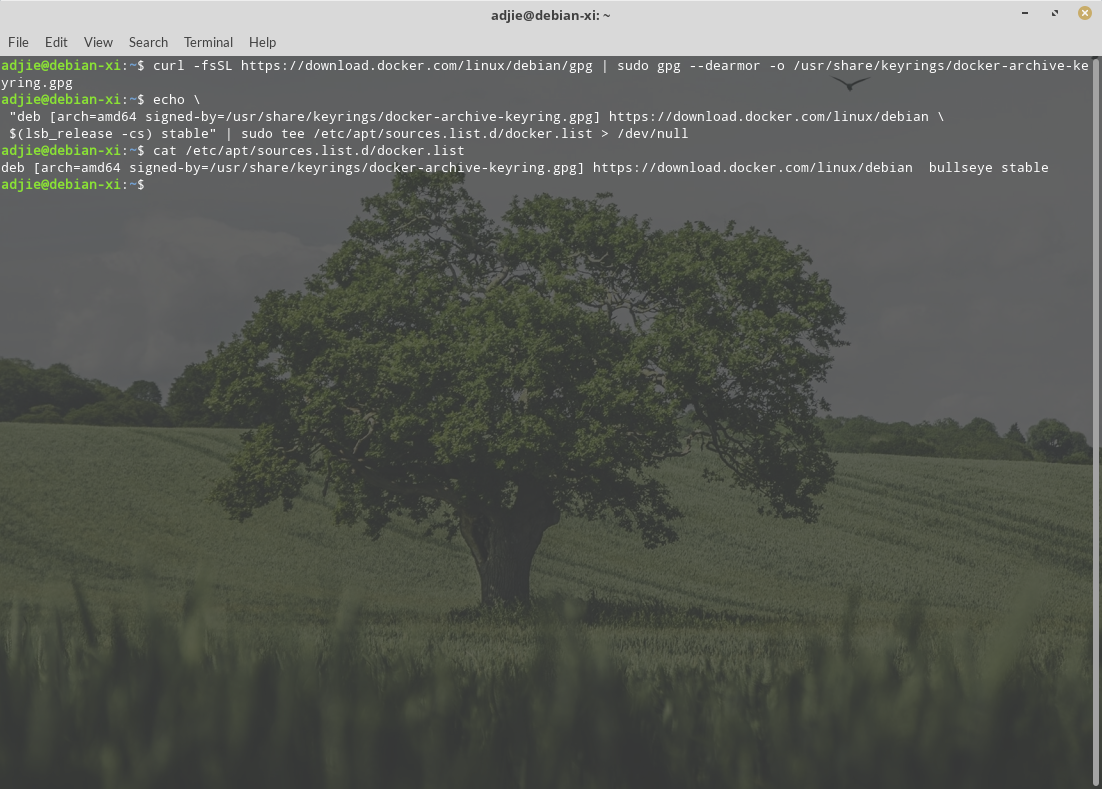
First, let's import Docker's GPG key into our system:
$ curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/debian/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpgNext, we need to create Docker's repository configuration file:
$ echo \"deb [arch=amd64 signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/debian \
$(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
Docker Installation
Now we're at the main installation process. We will install the latest version of Docker.
Update local package index:
$ sudo apt update
Before continue with Docker installation, if your system has Docker installed from the Debian repository before, you must remove it using the command below:
$ sudo apt remove docker docker-engine docker.io containerd runcThen install the latest version of Docker:
$ sudo apt install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
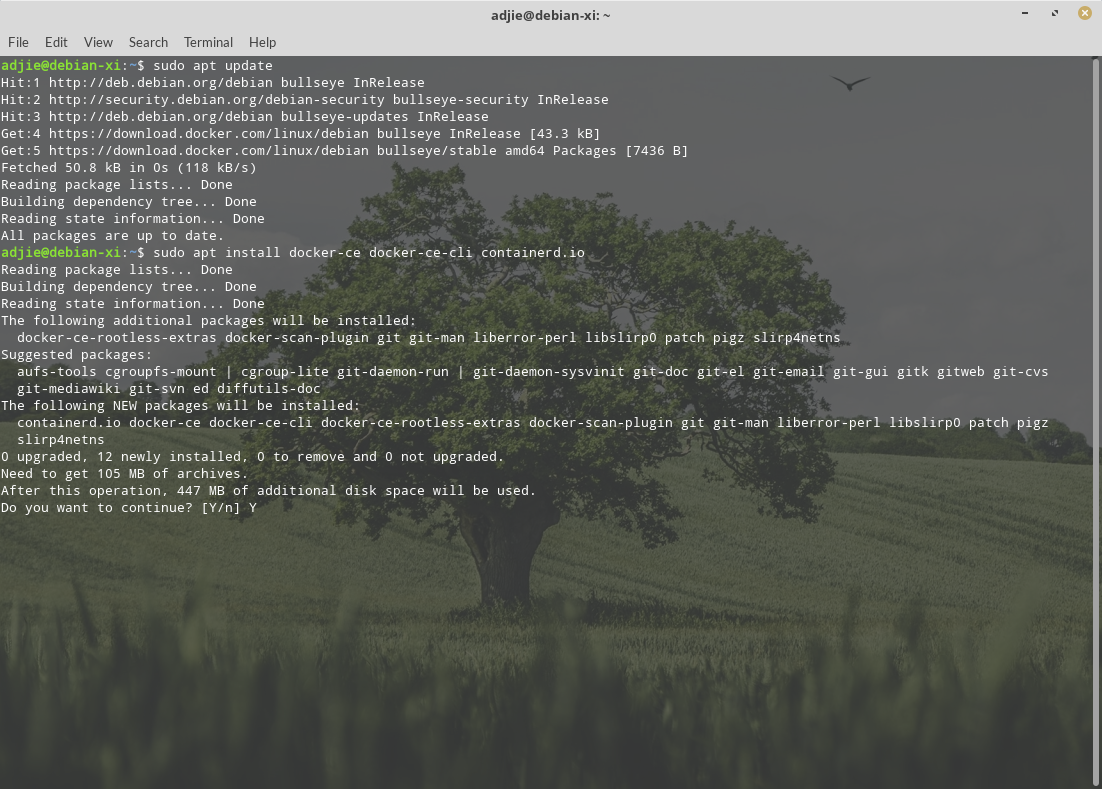
To continue with installation, press "Y" followed by "Enter".
Let's sit back and relax until this process completed. When it's completed, the docker
group is created but no users are added. To be able to use Docker, add
our normal user to the group to run Docker commands as non-privileged
user.
$ sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
To make this change effective, we need to log out and log back in so that our group membership is re-evaluated.
Verify Installation
Next step is verify that our installation is successful. Back to our terminal, enter this command:
$ systemctl is-enabled docker
$ systemctl is-enabled containerd
$ systemctl status docker containerd
If everything is correct, it should respond with something like below:
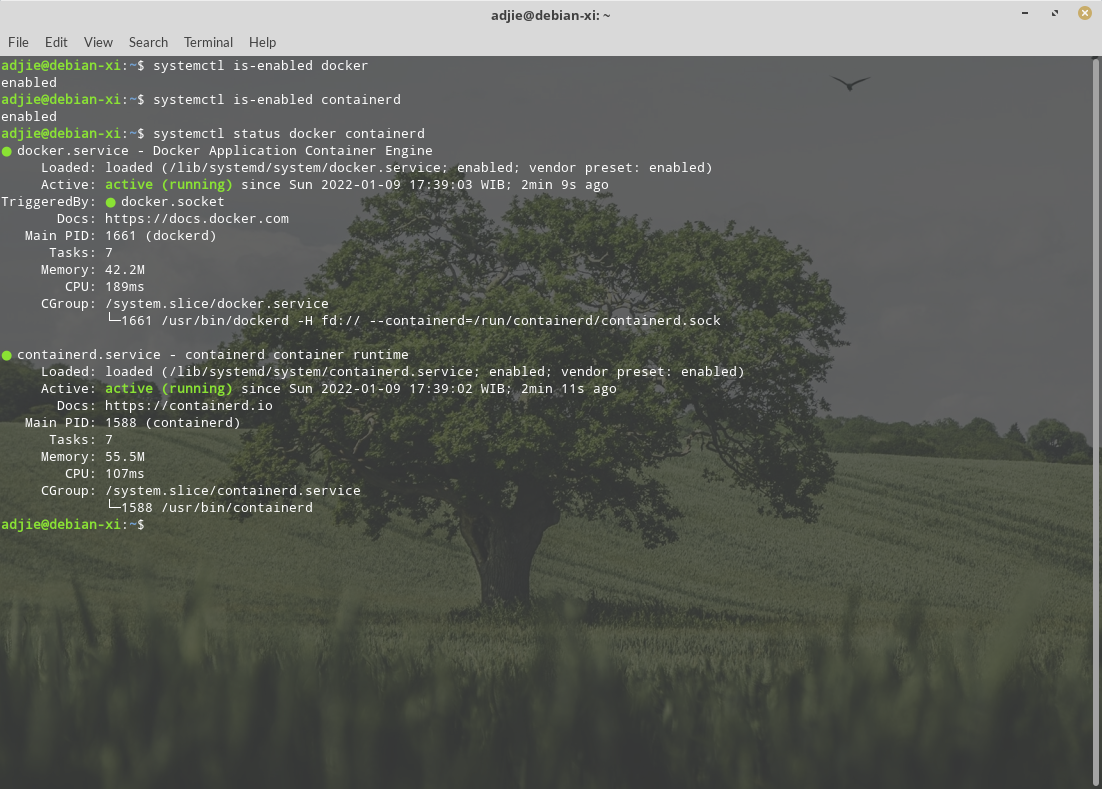
Now, let's run a test Docker container:
$ docker run --rm -it --name test alpine:latest /bin/sh
It should respond with something like this:
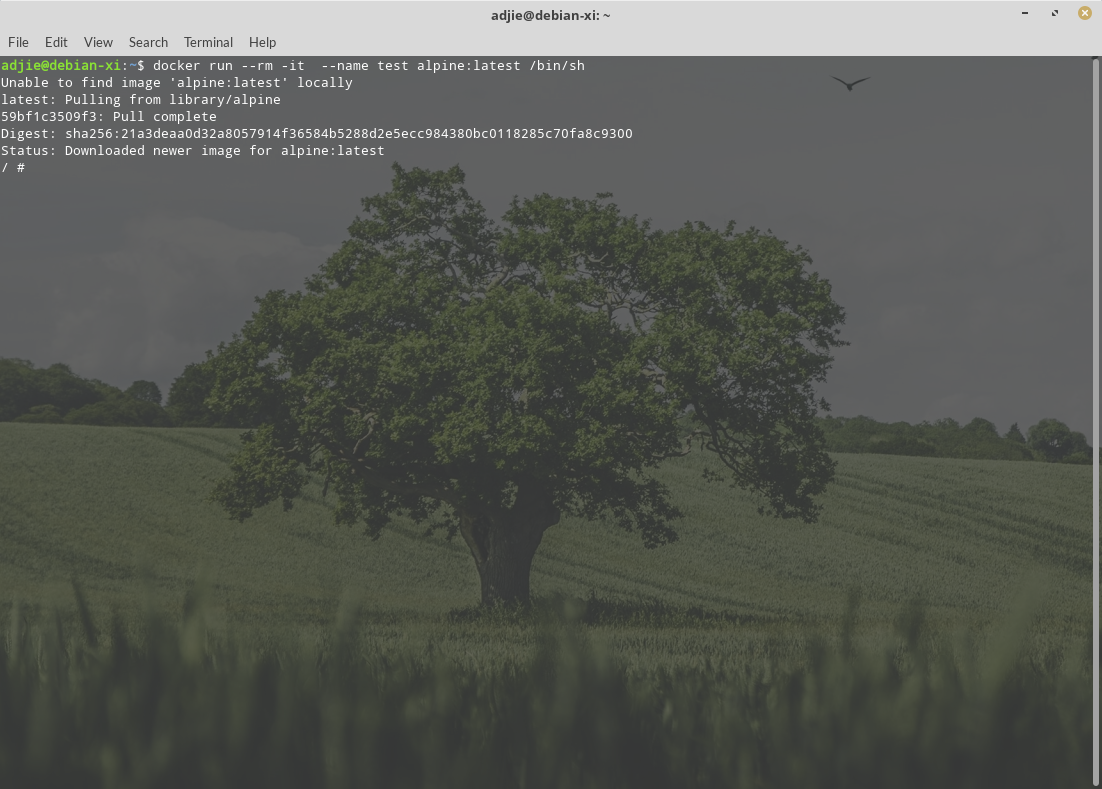
If it does, congratulations, we've successfully installed Docker Community Edition on our Debian 11 Bullseye.
Final Words
Well, that's it. I hope that you now know how to install Docker Community Edition on Debian 11 Bullseye. If you run into any issues or have any feedback feel free to drop a comment below.
